Plant-Based Protein Power: Delicious Recipes for All Dietary Needs
Exploring new ways to satisfy nutritional needs without compromising taste is an exciting venture for anyone adopting a plant-based lifestyle. As people transition towards diets rich in vegetables, grains, and legumes, the diversity of plant-based protein sources stands out. Rich in nutrients and capable of meeting diverse dietary preferences, plant-based proteins are essential for anyone seeking both balance and flavor in their meals.
A plant-based diet opens doors to a variety of delicious flavors and textures, enabling a nutritious and satisfying dining experience. With the rise of creative recipes, crafted from ingredients like lentils, chickpeas, and quinoa, it’s clear that there are numerous ways to enjoy these proteins while maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Recipes are available for every palate, ensuring that no one misses out on a well-balanced meal.
Whether for health reasons or environmental concerns, embracing a plant-based lifestyle can redefine food choices, leading to enjoyable meals rich in protein and essential nutrients. These recipes cater to individual dietary preferences, demonstrating how plant-based proteins can be both delicious and versatile. As more people discover these options, it’s easy to see how plant-based proteins can be effortlessly integrated into daily life.
The Basics of Plant-Based Protein

In the realm of nutrition, plant-based proteins are gaining significant attention due to their health benefits and sustainability. A key consideration is how they stack up against traditional animal proteins in terms of amino acid content and overall nutrition.
Understanding Amino Acid Profiles
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and crucial for various bodily functions. Proteins are composed of 20 different amino acids, nine of which are essential and must be obtained from the diet. Plant-based proteins such as lentils, quinoa, and chickpeas provide a diverse array of amino acids but may lack one or two essential components.
For instance, legumes are often low in methionine, while grains might lack lysine. Combining different plant proteins, like rice and beans, ensures a complete amino acid profile. Certain plant-based protein powders, like those made from rice and pea protein, enhance the amino acid content effectively. These combinations reinforce the nutritional quality, making plant-based diets more balanced.
Comparing Plant and Animal Proteins
Both plant and animal proteins offer essential nutrients, but they differ in their amino acid profiles and other nutrients. Animal proteins typically provide a complete set of essential amino acids, making them a traditional benchmark for protein quality. They also contain vitamins such as B12 and minerals like iron in bioavailable forms.
On the other hand, plant-based proteins are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, contributing to various health benefits including improved heart health and reduced inflammation. Pea protein, for example, is a common substitute known for being hypoallergenic and sustainable. While plant proteins may require strategic combinations to match animal protein amino profiles, they offer unique nutritional advantages.
Nutritional Advantages of Plant-Based Proteins
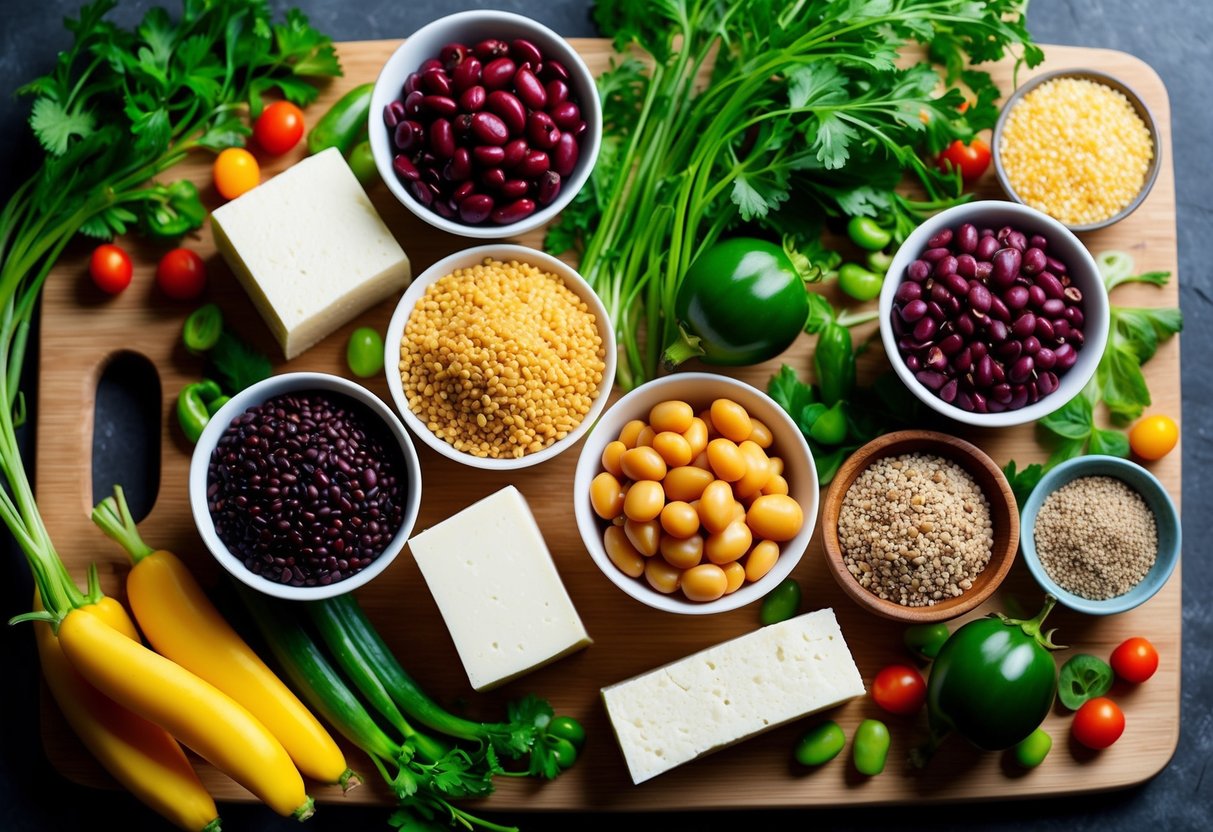

Plant-based proteins are packed with essential nutrients and offer numerous benefits that support overall health. These foods come with diverse macro and micronutrient profiles and contribute significantly to disease prevention and long-term wellness.